 |
| Concrete Shear Wall Design Spreadsheet |
Download Free Concrete Shear Wall Design Spreadsheet
What is a concrete shear wall?
In structural engineering, a shear wall is a vertical element of a seismic force resisting system that is designed to resist in-plane lateral forces, typically wind and seismic loads. In many jurisdictions, the International Building Code and International Residential Code govern the design of shear walls.
A shear wall resists loads parallel to the plane of the wall. Collectors, also known as drag members, transfer the diaphragm shear to shear walls and other vertical elements of the seismic force resisting system. Shear walls are typically light-framed or braced wooden walls with shear panels, reinforced concrete walls, reinforced masonry walls, or steel plates.
Plywood is the conventional material used in wood (timber) shear walls, but with advances in technology and modern building methods, other prefabricated options have made it possible to inject shear assemblies into narrow walls that fall at either side of an opening. Sheet steel and steel-backed shear panels in the place of structural plywood in shear walls has proved to provide stronger seismic resistance.
What is the minimum thickness of shear wall?
Minimum nominal thickness of masonry shear walls shall be 8 inches (203 mm). Exception: Shear walls of one-story buildings are permitted to be a minimum nominal thickness of 6 inches (152 mm).
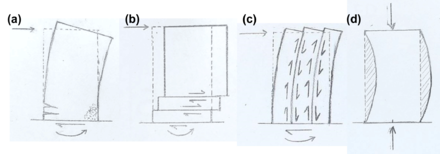
Loading and failure mechanisms:
A shear wall is stiffer in its principal axis than it is in the other axis. It is considered as a primary structure which provides relatively stiff resistance to vertical and horizontal forces acting in its plane. Under this combined loading condition, a shear wall develops compatible axial, shear, torsional and flexural strains, resulting in a complicated internal stress distribution.
In this way, loads are transferred vertically to the building's foundation. Therefore, there are four critical failure mechanisms; as shown in Figure 1. The factors determining the failure mechanism include geometry, loading, material properties, restraint, and construction.
 |
| Concrete Shear Wall Design |
Examples for Concrete Shear Wall
 |
| Concrete Shear Wall |
 |
| Concrete Shear Wall |
Download also:


Post a Comment